Abdullah Şamil Güser
Nodes
Master Node

- Kubernetes services and controller are located on the control plane
- They are also called the master components
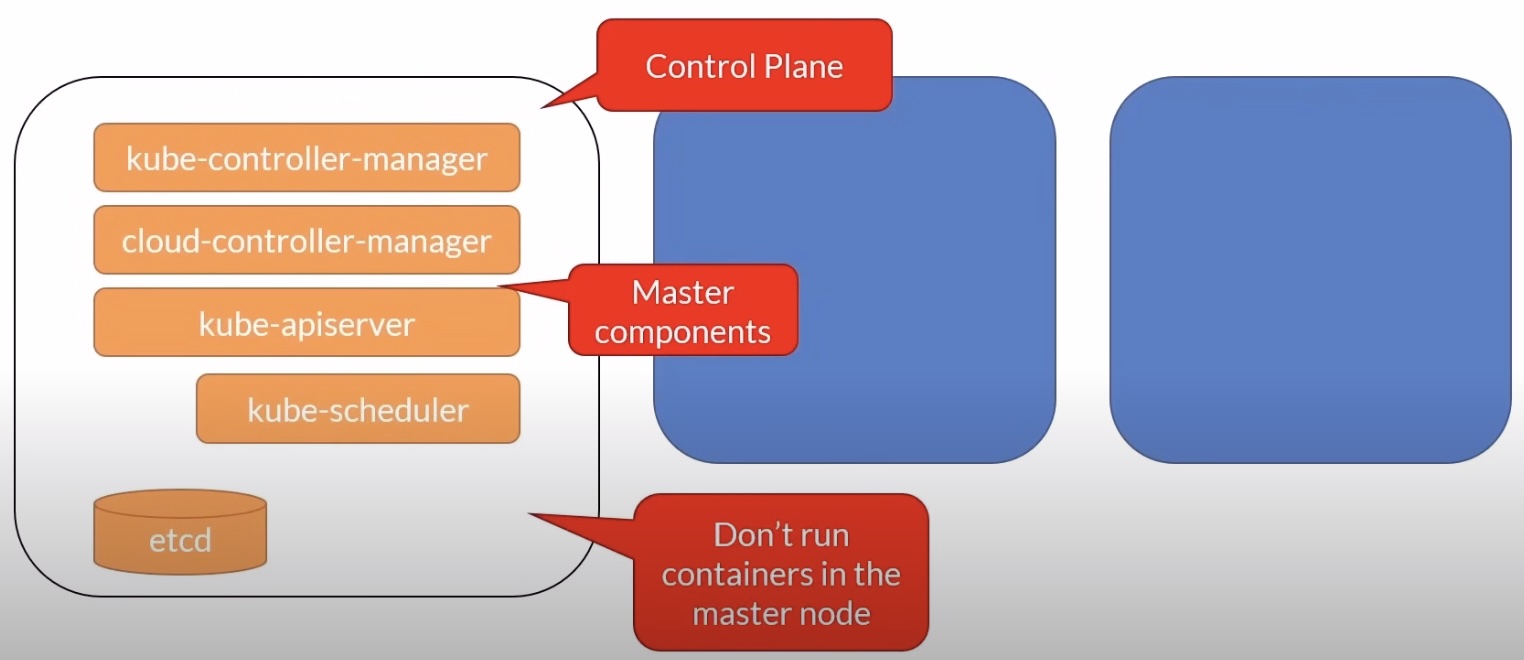
etcdis a key-value data store that stores the state of the cluster- The API Server (
kube-apiserver) is the only component that interacts withetcd
kube-apiserver
- It exposes a REST interface and client tools like the kubernetes CLI communicates through that API.
- Save state to the datastore (etcd)
- All clients interact with it, never directly to the datastore
etcd
- Acts as a datastore for storing cluster state
- It’s not a database but a key-value store
- It’s the single source of truth inside the kube cluster
kube-control-manager
- The controller of controllers!
- Runs other kube controllers
- Node controller
- Replication controller
- Endpoints controller
- Service account and Token controller
cloud-control-manager
Interacts with the cloud providers controllers
- Node : For checking the cloud provider to determine if a node has been deleted in the cloud after it stops responding
- Route : For setting up routes in the underlying cloud infrastructure
- Service : For creating, updating and deleting cloud provider load balancers
- Volume : For creating, attaching, and mounting volumes, and interacting with the cloud provider to orchestrate volumes
kube-scheduler
- Watches newly created pods that have no node assigned, and selects a node for them to run on
- Factors taken into account for scheduling decisions include
- Individual and collective resource requirements
- Hardware/software/policy constraints
- Affinity and anti-affinity specifications
- Data locality
Addons
You can install various add-ons on the masternode these add-ons provide additional functionalities in your kubernetes cluster.
- DNS
- Web UI (dashboard)
- Cluster-level logging
- Container resource monitoring
Worker Nodes
- A node is a physical or virtual machine
- A group of nodes forms a cluster
- There’s a special node called the masternode, it’s sometimes called the control plane where the kubernetes services are installed
- The nodes running the containers are called the worker nodes

- When a worker node is added to the cluster some kubernetes services are installed automatically
- These are services necessary to run pods and they are managed by the master components on the masternode
kubelet
- Manage the pods lifecycle
- Ensures that the containers described in the Pod specs are running and healthy
kube-proxy
- A network proxy
- Manages network rules on nodes
Container runtime
- K8s supports several container runtimes
- Must implement the Kubernetes Container Runtime Interface
- Moby
- Containerd
- Cri-O
- Rkt
- Kata
- Virtlet
Note : Container runtime - K8s V1.19+
- Docker images run as is. It’s business as usual!
- What’s changed is what you can do inside the cluster
- You can no longer access the Docker engine inside the cluster
- Docker commands won’t run if you ssh into a node
- Use crictl instead
Nodes pool
- A node pool is a group virtual machines, all with the same size
- A cluster can have multiple node pools
- These pools can host different sizes of VMs
- Each pool can be autoscaled independently from the other pools
- Docker Desktop is limited to 1 node
CLI Cheat Sheet
# Get a list of all the installed nodes. Using Docker Desktop, there should be only one.
kubectl get nodes
# Get some info about the node.
kubectl describe node